Layout of Excel
When you open Excel, it opens a workbook. A workbook is a collection of worksheets.
Below is a description of the different parts of Excel.
 |
-
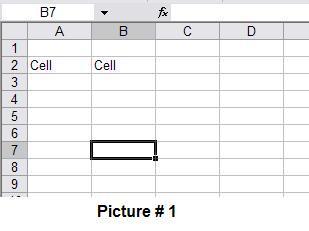
B7 indicates that is the cell that is selected.
-
To the right of fx is a box. This is where you can enter text or formulas at.
-
If you click on the fx, it will give you a list of formulas you can use and helps you set them up.
-
The columns are lettered starting at the Letter A to the left and continues up the alphabet.
-
The rows are numbered starting from top down starting at 1.
-
The headers are the cells with numbers or letters.
-
The numbered headers indicate the row.
-
The alphabetical headers indicate the column.
-
The darker box indicates what cell is highlighted. You will notice the alphabet letter that cell is located on is darker than the others. You will also notice that the number that cell is on is darker than the others. This means the cell is located on that column and row. As you can see in Picture 1, cell B7 is highlighted. needtodo
-
The sheet1, sheet2 and sheet3 are worksheets that is available to be looked at or used. You can rename the worksheets to what you want them to say.
-
If there is more worksheets than there is room to display, use the arrows to move between the worksheets. The arrows only moves the names. It doesn't change the view of what worksheet your looking at. To see the other worksheets, you will have to click on the name.
This allows you to create, open, or save a workbook. This also allows you to do various other tasks as well. Below is only a description of some of the icons.
-
Formula - To let Excel know you are typing a formula, type an equal sign ( = ) at the beginning.
-
Text - To let Excel know you want the cell to be text do not type an equal sign ( = ) before the text.
-
Cells do not wrap the text by default. If the text is longer than the cell, it will continue past the cell but it doesn't touch the next cell. For example, if you type in text in C4 and it goes past C5, C6, and C7 it doesn't touch C5, C6, and C7. If you type in text in C5 then the text will disappear on C4 that goes past C4. The text is still in C4. You just wont be able to see it.