Better Together: Using ISA Server 2004 with Exchange Server 2003
This article is from Microsoft
Attacks against IT networks are on the rise and becoming increasingly complex. Traditional firewalls are often inadequate to protect against the latest threats, exposing Internet-connected organizations of all sizes to operational and legal risks. You can mitigate threats and easily enable more secure remote access to services such as Microsoft Office Outlook Web Access by adding advanced protection for Exchange Server 2003 with Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server 2004.
More Secure Messaging
ISA Server 2004 and Exchange Server 2003 are designed to work closely together in your network to provide a more secure messaging environment. ISA Server acts as an advanced, application-layer firewall that controls Internet traffic between any number of networks that are connected to it. In the Exchange Server scenario, ISA Server inspects traffic entering your internal corporate network. When you use ISA Server to handle all inbound requests from client applications such as Microsoft Office Outlook 2003 and Office Outlook Web Access, your Exchange front-end servers no longer need to be located in the perimeter network, and your Exchange Server resources are protected from attack.
All inbound Internet traffic bound to your servers running Exchange Server is processed by ISA Server. This includes traffic such as:
- Outlook Web Access
- Remote procedure call over hypertext transfer protocol (RPC over HTTP) communication from Office Outlook 2003 clients
- Exchange ActiveSync
- Outlook Mobile Access
- Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3)
- Internet Message Access Protocol version 4 rev 1 (IMAP4)
When ISA Server receives a request from a client application such as Outlook 2003 to access information on an Exchange server, ISA Server routes the request to the appropriate Exchange servers on your Internal network. The internal Exchange servers return the requested data to ISA Server, and then ISA Server sends the information to the client through the Internet.
ISA Server 2004 uses forms-based authentication for all versions of Exchange Server, including versions prior to Exchange Server 2003. Once the mail server is published with ISA Server 2004, the ISA Server 2004 server generates the Outlook Web Access logon form for remote clients. This provides two key benefits:
- Elimination of cached credentials. ISA Server 2004 requires that remote users provide their unique logon name and password each time a new Outlook Web Access session is started. This helps ensure that even if a remote client is stolen or otherwise compromised, an attacker can not gain access to Outlook Web Access using a locally stored logon name and password.
- Pre-authentication of remote users. Only users that are authenticated by ISA Server 2004 at the firewall are allowed through to the Exchange Server. Anonymous logon attempts never reach the Exchange server.
ISA Server Features
ISA Server 2004 includes several features that complement and ease the publishing of Exchange servers.
-
New Mail Server Publishing Wizard. You can easily configure access rules that publish:
- Web client access
- Client access
-
Web client access. Mobile and remote access help you work conveniently from almost anyplace, anywhere:
- Outlook Web Access. Get more secure access through a Web browser that uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to view your e-mail messages, calendar, group scheduling, and public folder information on Exchange servers.
- Outlook Mobile Access. Gain access to Outlook from your mobile device.
- Exchange ActiveSync. Synchronize directly and with high levels of security to your Exchange Server mailboxes from Microsoft Windows–powered devices such as Pocket PC 2002, the Pocket PC Phone, and Windows Powered Smartphone.
- ISA Server also enables you to publish an RPC proxy server so that Outlook 2003 clients can gain access to their mailboxes using RPC over HTTP.
- Client access. ISA Server enables you to publish Exchange Server to allow direct client access on these protocols:
- RPC
- IMAP
- POP3
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) (to enable sending of e-mail messages)
Network Topology
The network topology (after moving servers out of the perimeter network) is shown in the following figure.
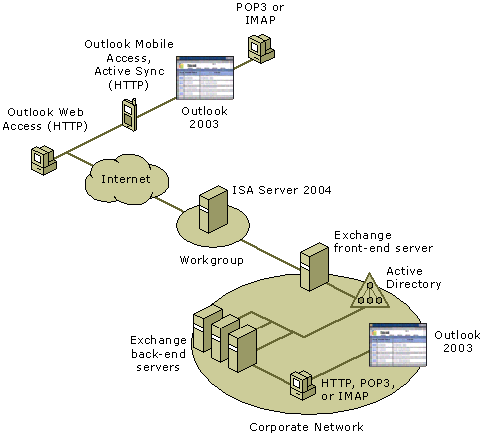 |
